Online Food Delivery and Takeaway Market Anticipated to develop with a sound development pace of over 16.20% over the gauge time frame 2018-2025. The Online Food Delivery and Takeaway Market are consistently developing over the world over the coming years. The significant driving element of worldwide Online Food Delivery and Takeaway market is access to an assortment of sustenance at one online market center and alternative to pay on the web and developing an interest for cleanliness quick nourishment.
Online Food Delivery Application Market Trends
The overall market for online food delivery application is picking up high from the base of smartphones being used. The expanding pervasiveness of cell phones for ordinary working has empowered the food business to use this vehicle for growing client base. Cafés, restaurants, food joints, and owners and franchisees of eateries selling services are utilizing food app as a creative method to draw in clients.
In the present fast-paced world, the association among organizations and end-buyers has assumed a vital job in the development of any business. The expanding number of online stages have prompted a quick change in food conveyance model crosswise over numerous pieces of the world, for example, in the Americas, Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. The food delivery procedure has changed from site requesting to utilizing food app from smartphones.
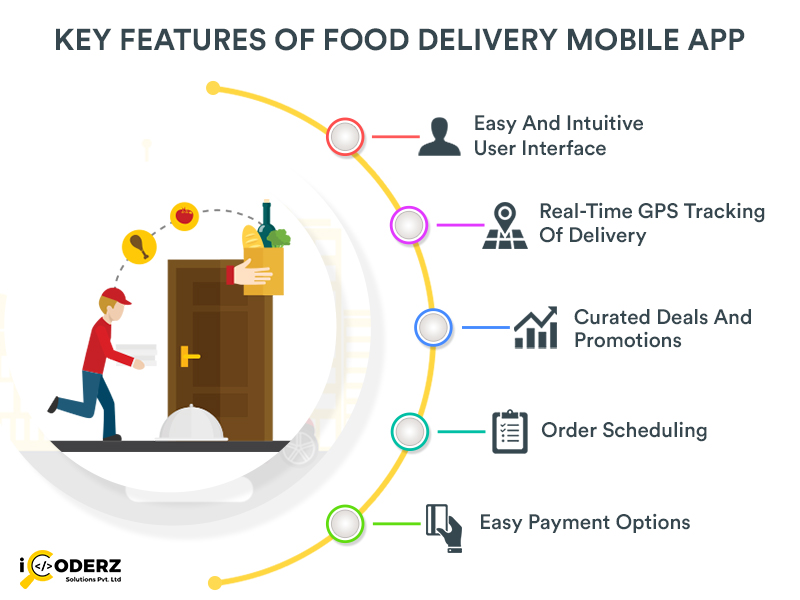
Considering technology trends, it creates a need to go for mobile app development for the food business section that is anything but difficult to pursue and are outwardly engaging is likewise boosting the market’s development. These applications are totaled stage that goes about as a mediator among cafés and clients and enable clients to access single or various eateries.
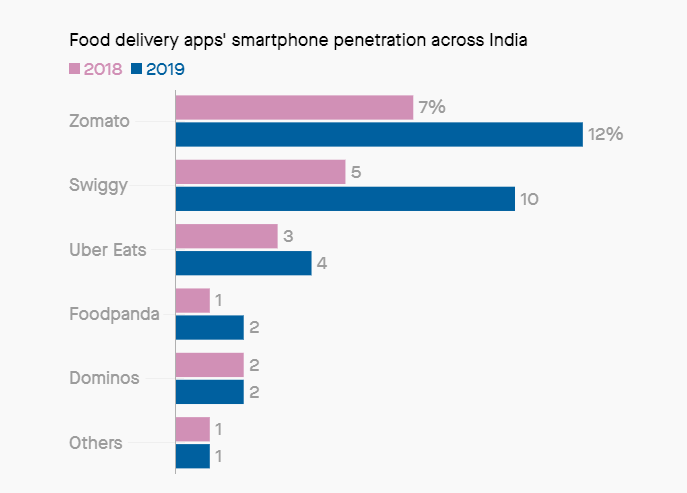
Infographics of Food Delivery App Usage
Source Url: https://scroll.in/article/930862/in-charts-who-leads-the-race-between-zomato-and-swiggy-and-where
These infographics show the penetrations and usage of food delivery apps via smartphones across India. Which food delivery app is used how much in 2018-19.
With many food apps coming up in the market it’s been easy to utilize and incorporate into your daily life. It helps with food ordering, table booking, online delivery or reservations. This ease can be easily adaptable by people around, which can never fail. The food delivery app market faces development challenges because of low Internet network on cell phones. Moreover, extra expense acquired by eatery or service, franchisee to dispatch a mobile application, and further for support, establishment, and promoting is constraining the development of Food delivery app market somewhat.
With the guide of innovation, a lot of information is delivered which is holding back to be broken down and designed. The bits of knowledge which can be mined from such a lot of information can empower organizations to develop at a pace based on their personal preference, be it long haul objectives or momentary objectives. Monitoring the market developments takes into consideration deftness and spryness is one of the most elevated evaluated attributes of current organizations.
Conclusion
These future scope has increased lots of opportunities for iOS app development and Android app development in Food business. Giving it the way convenient to users, there would arise a need for more and smarter phone apps in by 2025. One such firm remains same intact in the market is iCoderz Solutions who is a key player in mobile app development. Visit their website or contact them for more information.
Best On Demand Food Delivery Apps Development And Solutions
How to build on-demand grocery delivery app for today’s tech-savvy




9 comments