Get ready for takeoff! The world’s airports are incredibly busy. 71% of travelers now book flights online or via mobile apps. This is why flight app development is not only a technological decision but also a business one. This increase suggests a substantial rise in global travel.
For savvy travel tech companies and Airlines, developing a strong online presence is no longer optional; it’s essential to be a leader in this ever-expanding global market. Customers today desire more than just a reservation; they want fast, super-easy travel experiences.
Providing actual real-time information, however, presents a significant challenge for app developers, particularly for critical information such as flight delays and cancellations. This is because data constantly flows in and out of multiple sources of origin. The demand for high reliability and accuracy by users for their critical travel plans necessitates robust data pipelines and error handling. To build a flight booking app that meets these expectations, developers need to go beyond just coding. Creating a high-quality flight booking app is no longer just a matter of development; it’s a strategic process for overall business growth. This comprehensive guide will unveil the main characteristics, key technologies, and a step-by-step procedure for developing a flight application.
Why Are Travel Apps So Complex to Build?
Travel applications, particularly those focused on flight booking, are inherently complex. They are complex systems that manage real-time data from multiple sources, facilitate the safe movement of money, and offer a user-friendly experience. Developing a travel app requires considering unstable prices, dynamic statistics, and scarce but time-sensitive data without compromising security. This complex nature demands an efficient development strategy, as well as a focus on resilience and fault tolerance. A momentary API outage, for instance, cannot crash the entire booking process, given the high-stakes nature of travel data.
What Flight Booking App Features Should Your Application Have?
To distinguish your platform as the best flight booking app, it must offer a comprehensive suite of capabilities that simplify the user journey while providing powerful options. Here are the essential flight booking app features:
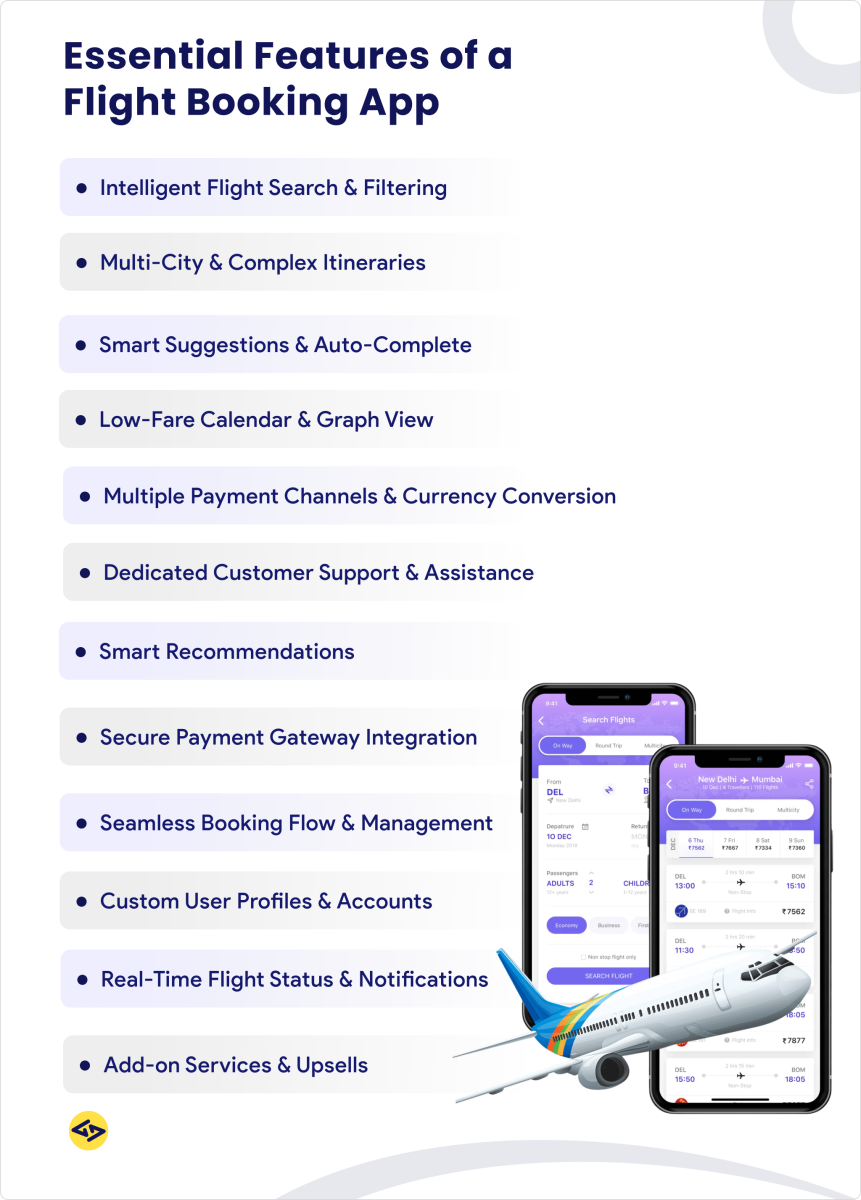
Intelligent Flight Search & Filtering:
- Core Functionality: Easy to use origin and destination, flexible or fixed date input.
- Advanced Filtering: Give users highly controllable powers, with filters, by airline, alliances, cabin class, number of stopovers, stopover time, departure/arrival moments, and price range. This is a key strength that leads to building a flight search application that actually benefits the user.
- Smart Suggestions: Automatic completion of airports/ cities, past searches, and hot routes.
- Multi-City/Complex Itineraries: The support of the user planning a multi-segment trip.
- Low-Fare Calendar/Graph View: Graphical representations to enable the user to establish the lowest-priced days to travel.
Seamless Booking Flow & Management:
- Transparent Flight Information: Show all flight info clearly—like baggage rules, seat space, and onboard services.
- Simple Passenger Forms: Easy-to-fill forms that can save passenger info for future bookings.
- Add-on Services: Let users easily add baggage, choose seats, order meals, or book extras like hotels and cars. These extras help increase revenue.
- Smart Recommendations: Use trip data to offer helpful extras (like travel insurance) at the right time.
- Final Review & Payment: Show a clear summary of the booking before completing payment.
Secure Payment Gateway Integration:
- Unique Insight: Since flight booking involves high-value transactions, the necessity of effective fraud detection and protection of secure payment gateways is difficult to overestimate. Payment security in this industry requires PCI DSS compliance.
- Multiple Payment Channels: The nurturing of credit/ debit cards, net banking, mobile wallets (Apple Pay or Google Pay), and even local payment services.
- Currency Conversion: Automatic show of prices in the currency that the user wants.
- Tokenization and Encryption: Activation of high-tech protective measures to safeguard confidential payment information. It is essential to integrate AI-powered systems to detect and avoid fraud.
Custom User Profiles And Account:
- Stored passenger: Details expedite future bookings.
- Reserved History & Future trips: Convenient access to the past and plans.
- Loyalty Program Integration: enable customers to integrate loyalty frequent numbers and check loyalty points.
- Notification Preferred: Alert preferences that can be customized.
- Individual suggestions: Utilising machine learning and user information to propose suitable flights or destinations.
Real-time Flight Status and Notification:
- Unique Insight: Delivering real-time flight status (delay, cancellation) and factoring this into the offering with good user satisfaction is the key. These notifications must be reliable and timely; when they are late or inaccurate, the user’s trust can be seriously compromised.
- Live Tracking: Maps in the app display the real-time position.
- Status Updates: Immediate updates of departure/arrival schedules, gate shifts, wheelchairs and terminal particulars, and baggage/baggage.
- Proactive Alerts: Push-based on check-in reminders, flight delays, cancellations, gate changes, and even boarding messages to improve user satisfaction to a large extent.
Dedicated Customer Support & Assistance:
- In App Chat/Messaging: Live line of communication in case of queries and help.
- FAQ Section: The area of self-service common questions.
- Emergency Contact Information: Information accessible on short notice in emergency cases. They should be integrated into CRM systems to have a unified view of the customer interaction across channels.
What Technologies Are Used to Build a Flight Booking App?
Building a powerful flight booking app is like constructing a modern airport – it requires several specialized components working together perfectly. Here’s a simplified look at the main technology “departments” that make it all happen:

Backend Systems:
- What it does: This is the unseen engine room of the app. It’s where all the complex calculations happen, like finding the best flight routes, managing user accounts, processing payments, and securely storing your information. It acts as the central hub for all the data.
- Key Technologies: Developers often use robust programming languages and frameworks like Java (Spring Boot), Python (Django/Flask), or Node.js (Express.js). These are chosen for their power to handle many tasks and users simultaneously, ensuring the app’s core logic is fast and reliable.
- Why it’s important: Without a robust “brain,” your app couldn’t find flights, remember your details, or process a booking reliably. It ensures everything runs smoothly and securely behind the scenes.
APIs & Data Feeds:
- What it does: Think of these as super-fast digital messengers and translators. They allow your app to talk to countless external systems, like airlines, global booking networks, payment processors, and even weather services. They pull in real-time flight availability, prices, and status updates, and send back your booking requests.
- Key Technologies: Your app primarily connects using APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) provided by major Global Distribution Systems (GDS) like Amadeus, Sabre, and Travelport, as well as direct APIs from individual airlines. For payment processing, secure Payment Gateway APIs from providers like Stripe, PayPal, or Razorpay are essential.
- Why it’s important: These connectors are why you can see millions of flight options from different airlines and get instant updates on delays. Without them, your app would be isolated and unable to access real-world travel data.
Frontend & User Interface:
- What it does: This is everything you see and interact with on your screen – the buttons, menus, search fields, maps, and flight information displays. It’s about making the app look good and feel intuitive and easy to use.
- Key Technologies:
- For apps built specifically for one platform (for top-tier performance): Swift/Objective-C for iOS (iPhones/iPads) and Kotlin/Java for Android phones.
- For apps that work on both iPhone and Android from a single codebase (often saving time and cost), Cross-platform frameworks like React Native or Flutter are popular choices.
- Why it’s important: Even with the most powerful “brain,” if the “display” is confusing or slow, users won’t stick around. A great user experience makes booking delightful, not dreadful.
Databases & Caching:
- What it does: This is where all the app’s information is stored. Some “memory” stores crucial, structured data like your passenger profile and booking history, ensuring it’s always accurate and consistent. Other parts of the “memory” act like a quick-access desk, temporarily holding popular flight searches or rapidly changing prices so the app can show you results almost instantly.
- Key Technologies:
- For structured, reliable data: Relational databases like PostgreSQL or MySQL.
- For fast, flexible data (especially temporary data or search results): NoSQL databases like MongoDB or Cassandra, and dedicated caching systems like Redis.
- Why it’s important: This ensures your data is safe, your past bookings are accessible, and searches are lightning-fast, providing a seamless and reliable experience.
Cloud Services:
- What it does: Instead of building and maintaining their giant computer server rooms, flight apps use “cloud services.” This means they rent powerful computing resources from huge, specialized data centers on demand.
- Key Technologies: Leading cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure. They offer everything from virtual servers and managed databases to specialized tools for scaling.
- Why it’s important: This “power grid” allows the app to handle millions of users at once, instantly scale up during busy holiday seasons, and operate reliably around the globe, all without massive upfront costs or maintenance headaches for the app owner.
What are the Steps to Develop a Flight Booking App?
The development of a successful flight booking app is an organized and iterative process, designed to mitigate risks and ensure quality.

Strategic Planning & In-depth Discovery:
- Market Analysis & Niche Identification: Who is your target user? What particular problem are you solving that is better than what currently exists? A robust flight app business plan with market size, competition, and value creation proposal would be key.
- Feature Prioritization: Define your Minimum Viable Product (MVP) for initial launch, followed by a roadmap for future enhancements. for initial launch, followed by a roadmap for future enhancements. An MVP for a flight app could include basic search functionality (origin, destination, dates), flight display, and a streamlined booking flow for a single passenger.
- Monetization Strategy: How will your app generate revenue? Common models include:
- Commission-based: Earning a percentage on bookings through GDS or direct airline partnerships.
- Markup: Adding a small margin to flight prices.
- Ancillary Sales: Revenue from selling add-ons like baggage, seat selection, and travel insurance.
- Advertising: Displaying ads within the app.
- Data Monetization: (Carefully, within privacy regulations) Leveraging aggregated, anonymized user data.
- Legal & Compliance Review: Understand international aviation regulations, data privacy laws (GDPR, CCPA), and payment industry compliance (PCI DSS).
Comprehensive UI/UX Design & Prototyping:
- User Journey Mapping: Understand how your users will navigate through all the application’s features.
- Wireframing & Mockups: Develop low and then high-fidelity visual depictions of the app’s interface.
- Interactive Prototyping: Build clickable prototypes to simulate the user experience.
- Usability Testing: Gather early feedback from target users to refine the design and identify pain points before development.
Robust Development & Iteration:
- Agile Methodology: Use an Agile method (Scrum, Kanban), in short development sprints. Agile emphasizes continuous collaboration, flexibility, and rapid delivery of working software, allowing for constant feedback and adaptability to change.
- Modular Coding: Design the application in standalone components to increase scalability, reusability, and maintainability.
- Version Control: Use systems such as Git to handle collaborative development and control of code.
- CI/CD: Continuously integrate and deliver code by automating the build, test, and deployment cycle to get a faster feedback loop and reduce mistakes.
- Complex API Integration: This is an ongoing and critical phase. Besides GDS and airline APIs, get connected to payment gateways, mapping services, notification services, and possibly CRM/analytics tools as well.
- API Management: Implement robust API management, including strong API key management, error handling, retry services, rate limiting (crucial for GDS calls), robust error logging, and circuit breakers to prevent cascading failures and provide reliability and traceability.
Rigorous Testing & Quality Assurance:
- Unit Testing: Verify individual code components.
- Integration Testing: Ensure seamless communication between different app modules and external APIs.
- System Testing: Validate the entire application against all functional and non-functional requirements.
- Performance Testing: Crucial for travel apps. Conduct load, stress, and scalability testing to ensure the app handles high user traffic and complex queries efficiently without degrading speed or responsiveness. Testing must simulate peak booking periods (e.g., holiday seasons, flash sales) to truly validate scalability.
- Security Testing: Perform penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and code reviews to identify and mitigate security risks.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Real users validate that the app meets business needs and is intuitive for them.
- A/B Testing: Continuously optimize features and UI elements based on user behavior data.
Conclusion: Ready to Launch Your Flight Booking App?
Building a flight booking app is a strategic investment with high potential. For Travel Tech Startups and Airlines, it presents a great opportunity to reinvent the digital travel experience. Success hinges on mindful app design, stable technical implementation, and familiarity with industry-specific details. The journey requires constant innovation, a commitment to quality, and an unwavering user focus. Ultimately, it comes down to designing a must-have tool to empower your business and its users. Maximize Your Software Quality with Our Testing Services. Contact us today to embark on your journey to build a travel app that truly makes an impact.
Ready to Build Your Flight Booking App?
Turn your travel business idea into reality with our proven solutions.

Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Key Challenges in Flight App Development?
Building a flight app is challenging due to the need for real-time data from various sources, ensuring secure payments, and fraud prevention. Developers must deliver a seamless user experience across platforms while navigating complex regulations. Finally, the app needs to be highly scalable to handle peak traffic and accurately manage dynamic fare rules.



